
Hello readers, in this blog we will learn about Brushless Motors also known as Brushless DC Motors or BLDC Motors. In this blog, we will discuss the working principle of BLDC motors.
What are BLDC Motors?
Brushless DC motors (BLDC)are widely used in various applications such as robotics, electric vehicles, drones, and industrial automation systems. Unlike conventional DC motors, BLDC motors do not have brushes, which makes them more reliable and efficient. Brushless DC motors are also known as electronically commutated motors (ECMs, EC motors).
BLDC motor is a permanent magnet synchronous electric motor which is driven by direct current (DC) electricity and it accomplishes electronically controlled commutation system (commutation is the process of producing rotational torque in the motor by changing phase currents through it at appropriate times) instead of a mechanically commutation system. BLDC motors are also referred to as trapezoidal permanent magnet motors.
Key Features of BLDC Motors
Brushless Operation
High Efficiency
Lightweight Design
Long Lifespan
Precise Speed Control
Lower Noise & Vibration
Low Maintenance
BLDC Motor Components and Construction
A BLDC motor has three main components: the stator, the rotor, and the Hall effect Sensor.
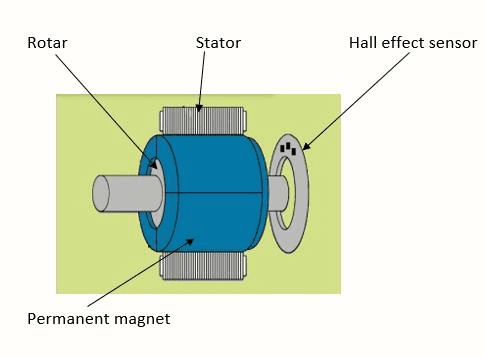
Stator
The stator is the stationary part of the motor that contains the windings. These windings are made up of insulated copper wire and are arranged in a specific pattern. The stator provides a magnetic field that interacts with the rotor to produce torque.
Rotor
The rotor is the rotating part of the motor that contains permanent magnets. The magnets are arranged in a specific pattern, opposite to that of the stator. The interaction between the magnetic fields of the stator and the rotor produces rotational movement.
Hall Effect Sensor or Electronic Controller
The Hall effect Sensor is the brain of the motor. It is responsible for controlling the flow of current to the motor windings. The controller also senses the position of the rotor and adjusts the current accordingly to ensure smooth and efficient operation.
Working Principle of BLDC Motor
The working principle of BLDC motors is based on the interaction between the magnetic fields of the stator and the rotor. The stator produces a rotating magnetic field, which interacts with the permanent magnets on the rotor, producing a torque that causes the rotor to rotate.

The Hall Effect Sensor plays a crucial role in the operation of the motor. It controls the flow of current to the motor windings based on the position of the rotor. The controller senses the position of the rotor using sensors or Hall effect devices mounted on the stator. These sensors detect the position of the magnets on the rotor and send signals to the controller.
Based on the signals from the sensors, the controller adjusts the flow of current to the motor windings to ensure that the magnetic fields of the stator and rotor are properly aligned. This ensures that the motor operates efficiently and smoothly, without any loss of power or vibration.
Advantages of BLDC Motors
BLDC motors offer several advantages over conventional DC motors. Some of the advantages are:
Higher Efficiency
BLDC motors are more efficient than conventional DC motors due to the absence of brushes. This results in less friction and lower power loss.
Higher Power Density
BLDC motors have a higher power density compared to conventional DC motors. This means that they can produce more power in a smaller size.
Longer Lifespan
The absence of brushes in BLDC motors results in less wear and tear, making them more reliable and durable.
Low Maintenance
BLDC motors require less maintenance compared to conventional DC motors. This results in lower maintenance costs and longer service life.
Applications of Brushless DC Motor
Brushless DC motors (BLDC) use for a wide variety of application requirements such as
Computer hard drives and DVD/CD players
Electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and electric bicycles
Industrial robots, CNC machine tools, and simple belt driven systems
Washing machines, compressors and dryers
Fans, pumps and blowers.
Conclusion
BLDC motors are becoming increasingly popular due to their efficiency, reliability, and low maintenance requirements. The working principle of BLDC motors is based on the interaction between the magnetic fields of the stator and the rotor, which is controlled by the electronic controller. With their numerous advantages, BLDC motors are expected to play an increasingly important role in various applications in the future.
If you are looking for Best in standard motors and other electronic components, reach out Campus Component today!
