Working on low-power embedded or IOT applications could become a bit challenging. They always need keen attention at all stages to keep power consumption the lowest possible because the device you are building should run for maximum time.
One of the most power-hungry components in your embedded/IOT could be the displays if your product has it. So, it is important to understand the power consumption of various displays before you select one. Whether you're tinkering with gadgets or diving into IoT projects, knowing about TFT, OLED, and Glass displays is important. Let's break down the basics and learn how to pick displays that won't drain our device's battery. In this article we will see how Power consumption differs from displays such as TFT, OLED, and Glass display(HDMI).
TFT Displays
TFT displays typically use TN (Twisted Nematic) type LCD technology, making them active-matrix LCDs. Active-matrix LCDs allow holding back some pixels while using others, ensuring the display operates with minimal energy consumption. TFT LCDs contain capacitors and transistors, crucial elements that contribute to the efficient functioning of the display. These components play a key role in utilizing a very small amount of energy, preventing the display from running out of operation. When we mention TFT LCD panels or screens, we're essentially referring to TN (Twisted Nematic) Type TFT displays. TFT, standing for active-matrix LCDs, represents a specific category within LCD technologies.
TFT displays boast wider viewing angles and a better contrast ratio compared to TN displays. This technology has found extensive use in various applications, including computer monitors, laptops, medical monitors, industrial displays, ATMs, and point-of-sale systems. In essence, TFT technology thrives on its active-matrix LCD characteristics, offering improved performance and versatility across a range of electronic devices. The power consumption of tft displays is composed of lcd panel, led backlit and touch screen, among which the power consumption of led backlight takes more than 90% of the whole tft screen, especially the high-brightness display module.
OLED Displays
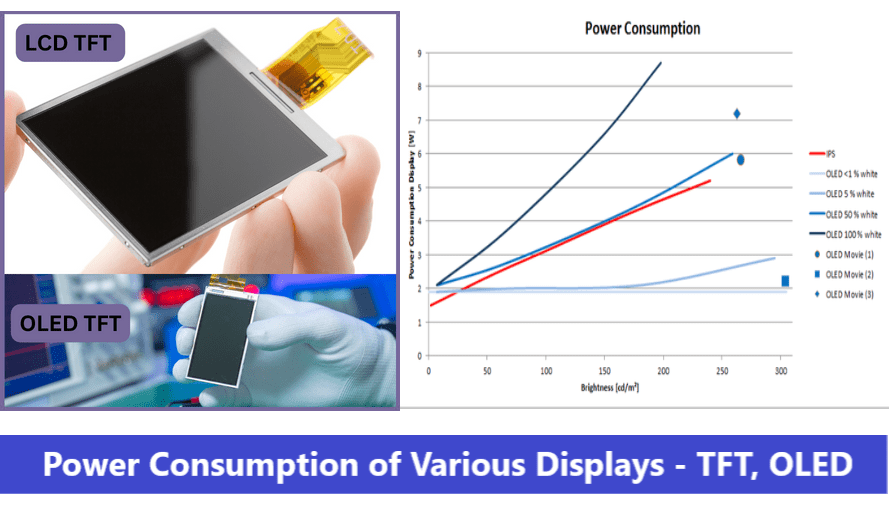
OLED displays stand apart as emissive display technology, distinguishing themselves from LCDs. Each illuminated dot on the OLED display creates a small, bright area with glowing phosphor, contributing to its unique visual appeal. OLED displays are renowned for their exceptionally high contrast, making them a preferred choice for high-end applications. Some of the most sophisticated TVs and mobile phones feature AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes) displays, emphasizing their premium status. OLED technology surpasses LCD in various aspects, offering better color reproduction, image quality, and a broader color gamut.Importantly, OLED displays consume less power compared to LCD technology.
OLED encompasses both AMOLED and PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes). When choosing for TVs and mobile phones, opting for AMOLED is recommended over PMOLED for enhanced performance. For those with a bit more budget, incorporating a touch screen into the display is an option. All these technologies are part of the family of Flat Panel Displays, distinguishing themselves from the bulky, heavy, old-fashioned, and expensive CRT (Cathode-Ray Tube) displays.
OLED and AMOLED displays consume more power as you turn more pixels on. This is because each pixel is composed of three tiny LEDs (four in some LG TVs), which emit their own light. With every pixel off, the display will only draw enough current to keep the controller chip running. The chip itself only needs a few milliamps.
In summary, OLED displays bring futuristic charm to visual experiences, offering superior contrast, vibrant colors, and energy efficiency. Whether you're choosing between AMOLED and PMOLED or contemplating touch screen integration, understanding OLED technology opens doors to cutting-edge display solutions.
Glass Displays
Actually, Glass display technology is a kind of TFT display with thin film transistors for individual pixels. But Glass displays have superior high contrast, wide viewing angle, color reproduction, image quality etc. Glass Display screens have been found in high-end IOT and Embedded applications, like manufacturing industries, cars, mobile phones, EV Vehicles, etc.
Both TFT LCD displays and Glass displays are active matrix displays, neither of them can produce color, there is a layer of RGB (red, green, blue) color filter in each LCD pixel to make LCD showing colors. LED backlights are usually together with them in the display modules as the light sources. Besides, both TFT screens and Glass display screens are transmissive, it will need more power or more expensive than passive matrix LCD screens to be seen under sunlight.
Glass Display screens transmittance is lower than TFT screens, lower power is needed for Glass display displays compared to TFT displays.
Conclusion
As we discussed above, the conclusion is if you need the lowest power consumption, OLED and glass LCDs are the best. Also you must have a power gating mechanism to reduce further power when the display is not in use. Understanding the power consumption parameters of TFT, OLED, and Glass displays is crucial for choosing a perfect display. Whether you prioritize energy efficiency, visual quality, or a balance of both, the right display technology can enhance user experience while minimizing environmental impact.
If you are building an IOT or Embedded device and looking for displays which can save your power consumption, We at Campus Component- electronic components shop pune, provide displays from popular brands such as Sinda, Nextion and DWIN to incorporate in your project.
